Empty Combs
The differences in empty comb and their role in spreading AFB
Empty, drawn comb is less likely to carry large numbers of AFB spores than is comb containing brood, or wet comb from honey supers.
The only exception is frames from the brood chamber of an AFB infected colony that has died, either from the disease or other reasons. These frames can contain AFB scale (the dried remains of diseased larvae or pupae), and are therefore very likely to transfer the disease to a new colony.
Videos
Our videos cover everything from your legal obligations to how to recognise AFB, collecting cell and bee samples and more.
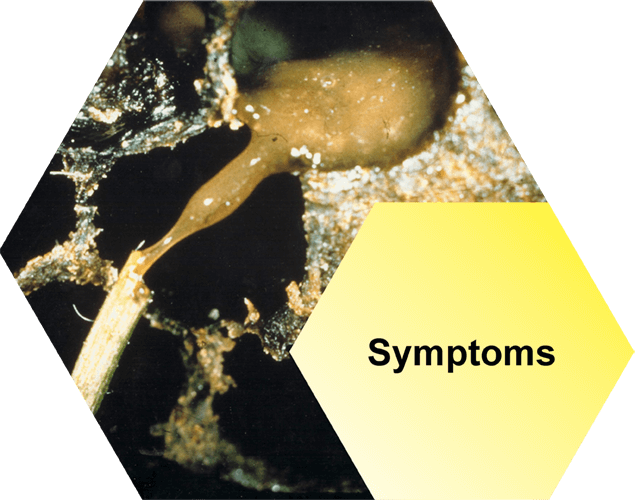
Symptoms
There’s a lot of good information here, telling you everything you need to know about recognising AFB: the visual symptoms, smell of AFB and more.
Inspection and Diagnosis
Successfully eliminate AFB by telling the difference between symptoms of AFB and other brood diseases in the hive. We tell you the best methods for inspecting your hives.
The Law
New Zealand beekeepers have a number of legal obligations that must be met regarding AFB disease. Read the shortened list in summary, here.
Elimination
Most hives become infected because bees, honey or equipment have been put into a hive from another hive that is infected with AFB. Lower your chances of an AFB infection by reading this section.
AFB Recognition Course Info
Find out when the next AFB Recognition and Competency Courses, or Refresher Courses are available. These are held throughout the year in various New Zealand locations across the South Island and North Island.
The AFB App
Follow the link below to open the App. Once open to save to your device you need to bookmark the URL on your phone so you can find it easily again. Please click here to open.